Ransomware has disrupted the cyber security landscape in devastating fashion. The trend that initially picked up steam in 2017 re-emerged to reap even more havoc amid the global pandemic caused by the COVID-19 outbreak. While many companies rushed to accommodate the remote workforce, they inadvertently created holes in their existing cyber security defenses―—holes that were inevitably exploited by opportunistic cyber criminals.
According to security researchers, ransomware attacks jumped by nearly 500 percent since the pandemic began in 2020. Moreover, the ransom fee reportedly increased to an average of $200,000 USD, a 43 percent increase from the average reported in the final quarter of 2020. The rise in activity has been accompanied by an increase in damage as attackers have adopted even more ruthless extortion tactics to extract money from desperate victims.
Ransomware Prevention
Byte for byte, ransomware is arguably the most dangerous form of malware in existence. Its ability to cripple organizations by holding IT assets hostage and draining corporate budgets has empowered hackers with quite the one-two punch. This is certainly a case where prevention is the best form of protection. On that note, we have outlined five effective ways to stop ransomware in its tracks.
1. Cover the Bases
At its core, ransomware is just another form of malware. As such, most variants are easily detectable by common anti-malware software. Some programs even come equipped with features that specifically target ransomware. Blended with proven defense systems such as firewalls, intrusion detection, and filtering at the web and email levels, rest assured that basic security measures can prove adequate in the ransomware prevention department.
2. Adopt Advanced Cyber Security Practices
Although most ransomware can be stamped out by solid anti-malware defenses, there is always a chance that cyber criminals will strike with complex attacks. For this reason, it makes sense to consider ramping up the sophistication of your ransomware prevention tools.
Advanced cyber security tools come from various schools of thought. A prime example is the zero-trust framework (see image below), which operates on the premise that no device (or user) should be entrusted with unfettered access to the network. This concept aids ransomware prevention by using a centralized agent, typically a software application or hardware appliance, to delegate network access to company devices based on identification and context.
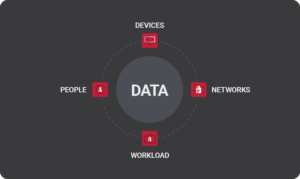
Implementing a state-of-the-art the cyber security infrastructure is rarely a low-cost endeavor. However, it’s the sort of investment that pays huge dividends in peace of mind.a
3. Roll Out a Ransomware-specific Educational Program
In most cases, ransomware attacks make their mark by taking advantage of oblivious end users. Maybe it’s an employee who takes the bait dangled in a phishing attack―—or executes the malicious payload by opening a seemingly innocent email attachment. These exploits, which fall in the social engineering category, rely on the combination of human intervention and curiosity to bolster the effectiveness of their attacks by tenfold.
A training program that educates end users on the core tenets of ransomware prevention is imperative. This program should address the following areas:
Email security: While social media is all the rage, email remains the most widely used means of communication. As such, it is a prime target of ransomware attacks. Make sure employees are up to speed on fundamentals such as verifying senders, and approaching links and attachments with extreme caution. It is not uncommon for malware to exploit whitelisted contacts, so employees should adopt the habit of scrutinizing any and all calls to action.
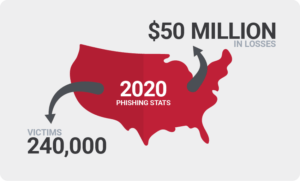
Phishing: One of the most common social engineering techniques, phishing uses fraudulent emails to trick unsuspecting recipients into either sharing sensitive information, or triggering the execution of malicious software. The FBI cited phishing as the most reported internet scam of 2020, accounting for more than 240,000 victims and roughly $50 million in losses.

Phishing scams are becoming increasingly difficult to spot, as they typically disguise their malicious intentions by mimicking the look and feel of trusted brands. A thorough education program will not only teach users how to spot these elaborate schemes, but go the extra mile by implementing phishing simulations that test their awareness.
Password protection: The proliferation of online services has made password management a drag. That doesn’t make it any less critical to cyber security. Highlighting the proficiency of today’s hacking tools, which are capable of randomly generating millions of possible combinations per second, is a good way to help users understand the importance of employing unique passwords that are difficult to guess.
4. Always Backup Your Data
Cyber criminals typically use ransomware to hold sensitive data hostage until the victims fork over a handsome ransom fee. If you’re not the type to negotiate with digital terrorists, you may earn a slice of solace from knowing that a potential breach can be mitigated by restoring your data from backups. Ideally, your backups are stored in a safe location―—be it in the cloud, or on a USB drive in a remote facility―—and can be recovered to a point that is not impacted by ransomware attack.

While a backup plan is indeed formidable, it is not the end all to ransomware protection. For starters, recovery may roll back to a point where your system is free of ransomware, yet still vulnerable to the same flaws that led to the attack. What’s more, like you, cyber criminals learn and evolve with the ever changing landscape. Realizing that recovery is an option, some have resorted to extracting data from targeted systems. This method acts as a sort of insurance policy that further strengthens their extortion tactics by threatening to leak the information if a ransom isn’t paid.
5. Take Out a Cyber Security Insurance Policy
The uptick in ransomware attacks and the cost prohibitive implications behind them has put cyber security into focus. Like traditional auto or homeowner’s insurance, cyber security insurance exists to mitigate the losses that result from security breaches. In theory, a robust policy will actually help organizations bolster their security defenses. For instance, insurance firms typically provide more coverage to companies that demonstrate a dedication to best security practices and preventative measures.
When it comes to cyber insurance, it’s imperative to know that not all policies are created equal. Some policies cover damages from a wide range of threats, which may include losses incurred during a ransomware attack. Moreover, some insurance providers have introduced policies that specifically address ransomware-related breaches. That said, there is no standardization in the cyber security insurance market. Policy terms can vary greatly in the way of coverage options, premiums, and deductibles. Make sure you understand the conditions and language before deciding on a plan.
Stay Safe!
Ransomware has proved to be a gamechanger for companies of all sizes. While there is no single method to stop this rapidly evolving threat in its tracks, there are viable solutions. By harmonizing multiple security tools and strategies, you can devise an integrated defense system that not only improves your ability to recover from a ransomware attack, but avoid this nuisance altogether.