Every day, people share information across public wires that travel through a series of third-party databases. Even though it’s an open system, we continue to exchange personally identifiable information like credit card numbers, bank information, passwords, and emails. Between our smartphones, tablets, and other devices, we have data traveling through many connections – so, how do companies and individuals keep their information private? The answer is complicated, but luckily, there’s a powerful tool to help protect transmitted information: Encryption.

What is Encryption?
Encryption is one of those words that gets thrown around a lot, but what does it actually mean? In layman terms, encryption is a way of scrambling data so that only those with an authorized key can open and unscramble it. To achieve this, computers convert plaintext (human-readable information) into ciphertext (incomprehensible data). Once this is accomplished, cryptographic keys are created, and there is generally one for the sender and one for the receiver – depending on the type of encryption. When the encrypted key is used to open the message, the data reverts to its original message. Thus, any message sent and opened without a key will appear as a jumbled mess of indecipherable information.
What Are Cryptographic Keys?
A cryptographic key (or digital key) is a string of values stored in a file, used by a collection of algorithms to lock and unlock data. Cryptographic keys allow the sender a deeper level of security when sending personally identifiable information. There are two different types of encryption keys. 1) Symmetric – a single private key the sender must share with the recipient. 2) Asymmetric – this has both a public key and a private key; the public key is shared, and the private key is kept hidden.
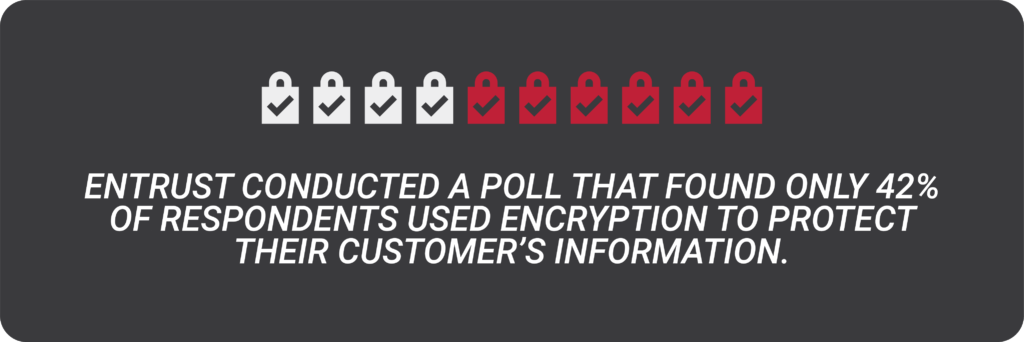
Encryption can be used on your devices like smartphones and fitness watches, online accounts, and is available through software and hardware—devices like encrypted flash drives, hard drives, and thumb drives. Using encryption helps protect your information from those trying to steal personal data.
What Is an Encryption Algorithm?
Algorithms are a process or set of rules used for calculation and as a way to solve problems, generally by a computer. For example, an Encryption Algorithm is the process of turning plaintext into ciphertext.
What Are the Different Types of Encryption?
- RSA – Rivest–Shamir–Adleman – An asymmetric key considered the best key encryption algorithm.
- AES – Advanced Encryption Standard – A symmetric key is considered one of the best encryption algorithms.
- Blowfish – A widely acclaimed software symmetric block cipher accessible to the public.
- Twofish – Another symmetric block cipher known for its flexibility.
- FPE – Format Preserving Encryption – Allows the format to stay the same when data is reverted from ciphertext to plaintext.
- SSL – Secure Socket Layer – This encrypts links between servers and browsers, identifiable by an https:// and/or padlock icon in the URL.
Do You Really Need Encryption?
Yes. The good news is that many websites already implore this and many devices have built-in encryption, so you have a layer of protection in many circumstances. However, with the constant cyber attacks, the best way to prevent a data leak is to protect your information before it enters cyberspace. Does it seem complicated? The short answer is yes, but the good news is that there are teams of experts constantly fighting this problem and developing tools to make this troubling situation less worrisome. In the coming weeks, we’ll be sharing more information about cybersecurity and what you can do to protect your data. Be sure to follow us here so you don’t miss out on any of this content.
Are you worried about security? Datalocker has you covered. Learn more here.