From cloud computing to mobile devices, the US government is powered by the same technology that drives industrial America. The biggest differences lie in regulatory requirements. Agencies in the government sphere, and the vendors that cater to them must adhere to standards that are far more strict than those mandated to non-government firms. TAA compliance is a classic example of such distinctions.

TAA compliance mandates that government agencies obtain products and services from jurisdictions covered under the federal Trade Agreements Act enacted in 1979. This goes for USB drives and other storage media as well as PDF readers and the simplest of software programs.
Dictated by the General Services Administration (GSA), it states that said offerings must originate from the US, or a location on its list of approved countries. Failure to meet TAA compliance can result in severe penalties, including a loss of federal contracts and millions of dollars in fines.
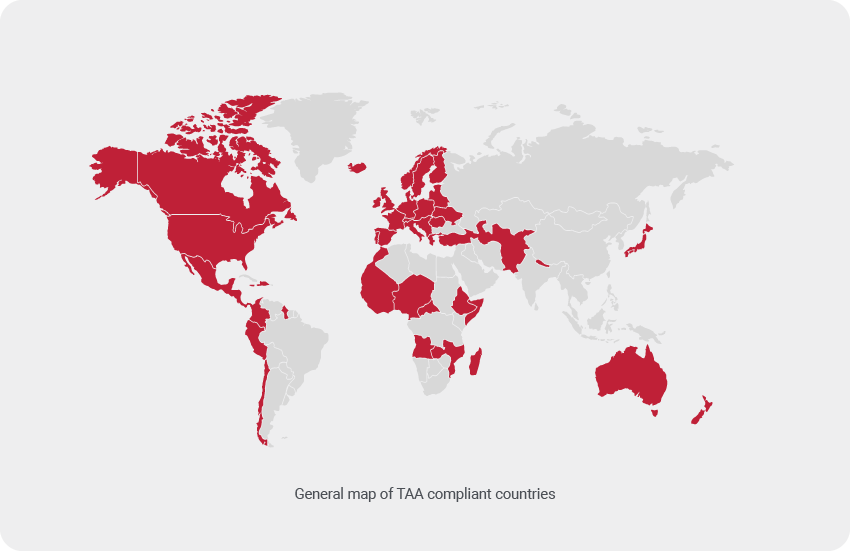
Like any legislation, the language included in the TAA is both specific and complex, starting with the country of origin. Nations on the designated list are validated through existing US trade agreements, and thus considered reliable sources of procurement.
Implications of the standard span across four internationally recognized categories:
- World Trade Organization Government Procurement Agreement countries
- Caribbean basin countries
- Least developed countries
- Free trade agreement countries
Perhaps the most important aspect of TAA compliance is understanding which countries haven’t been whitelisted. This is critical because the forbidden list includes some locations you might not expect to find. For instance, China, despite being a long time trade partner of the US, is excluded due to a number of unresolved diplomatic issues. Also noticeably absent is Russia, widely recognized as the ransomware capital of the world.
Another fundamental component relates to production. According the TAA, goods and services must be manufactured, or substantially transformed in a signatory country. The term “transformed” is particularly vague, but generally refers to additions or alterations made prior to completion of the end product. Not withstanding, TAA compliance is determined via detailed investigation and analysis of the product or service in question, and therefore, the process varies from one case to the next.
How TAA Compliance Impacts Business
Companies that fail to prove TAA compliance run the risk of losing their GSA contracts and violating the False Claims Act. This is no mere loss of opportunity. Medical supply firm Ambu is one example of a company that paid heavily for its failure to meet TAA compliance — to the tune of $3.3 million!
TAA compliance benefits both the government and the businesses that service it. Sure, navigating all the red tape can be a real pain, but those that endure the process have plenty to gain.
The TAA Advantage
Brand recognition: TAA compliance is a ringing endorsement for any business. In essence, it acts as the seal of approval that speaks to the quality and reliability of a given product.
Exclusive revenue opportunities: Upon achieving compliance, companies unlock access to a lucrative marketplace that is exclusive to the government. A report published by Bloomberg Government estimates that the White House requested an , which marks a record high. This is particularly good news for distributors of compliant goods and services.
Attractive pricing: The government marketplace adheres to strict industry standards. Compliant products are deemed fairly priced by GSA scheduling, which means vendors instantly gain the benefit of competitive pricing.
Quality procurement: By default, TAA compliance eliminates low-quality offerings from the equation. As a result, businesses can stand by their claims of servicing government clientele with the best breed of products and services.
Validating TAA Compliance
If you’re in the market for USB drives or other TAA compliant products, you should know what to look for when browsing the marketplace. Some vendors will showcase the results of certification analysis on their company websites to verify compliance. DataLocker is transparent in highlighting its credentials for the most stringent industry regulations. In fact, any vendor claiming TAA compliance should be willing to provide official documentation to prove it upon request.